5 Major Challenges for EV Manufacturers
Business | October 13, 2022 | By
According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, transportation accounts for about 23% of global energy-related greenhouse gases, and of that, road transportation is 72%. In an effort to prevent the rising effects of climate change, many countries have planned to slowly phase out Internal Combustion Engines (ICEs) by 2030-2040, with a shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) powered by rechargeable batteries specific to EVs. For example, the European Union’s (EU’s) “Fit for 55” program aims to align climate, land use, energy, transport, and taxation policies to reduce greenhouse emission gases by at least 55% before 2030, and the Biden administration’s 50% EV target by 2030. In addition to these mandates, many governments are also offering EV subsidies.
In the fight against climate change, the next 2 decades will be transformative and crucial for the automotive industry. Also, the opportunity for electrification in all automotive segments is huge. But the pace might differ across segments. All said and done, widespread adoption of EVs is a must to curb GHG emissions. So, it’s important to launch new EVs faster in the market.
Scott Keogh, chief executive of Volkswagen Group of America, told an Automotive News forum in Washington that the move to EVs is the single biggest “industrial transformation in America.” However, this brings with it a whole new set of challenges.
The Challenges in EV Manufacturing
Achieving EV Scalability
In the US, EVs make up only 6% of the new cars delivered in H1 2022. So, to meet the 50% target by 2030, companies have to scale up production. We know that batteries are one of the key components of an EV. Currently, the US is manufacturing very few number of batteries a year. But, the manufacturers are trying to ramp up production. However, to meet the set target, they have to scale their production capacities to enormous quantities. To make this happen, automakers, battery companies, and the like have committed tens of billions of dollars to build a new battery and EV assembly plants to scale up production.
For companies to scale up production, they can either go with the brown field or green field approaches. In a brownfield approach, manufacturers find out ways to retain at least the common facilities such as paint or body shop to minimize capital spend. When it comes to the green field approach, companies invest from the ground up to set up specifically designed manufacturing plants such as the plant layouts, attracting the right set of talents, developing suppliers, sourcing the right materials, and setting up supply networks.
Attracting the Right Set of Talent
According to Keogh, attracting the right talent is one of the critical challenges. He said that US manufacturing needs to do more to boost manufacturing capacity. Why? During the Covid crisis, manufacturing capacity has fallen from more than 17 million in 2000 to 12.8 million. But is slowly rebounding to pre-pandemic levels. Keogh said that America needs to focus more on manufacturing rather than on the service industry. And according to him, it will be a challenge to take someone working in a Starbucks and place them in a factory environment.
Challenging the Traditional Automotive Supply Chain
An expansion in the EV market poses a serious threat to the legacy automotive supply chain. Major components such as the traditional transmission systems, exhaust, and fuel systems that are required only for ICEs, are absent in EVs. This means that suppliers of all these components face a serious threat of extinction if they do not adapt quickly to manufacture components for EVs.
According to Mckinsey, these components would shrink to 11% by 2030, which is about half the 2019 number. And according to the Institute for Economic Research (Ifo) in Munich, more than 1 lakh jobs will be affected by the phase-out of coal power in Germany by 2038.
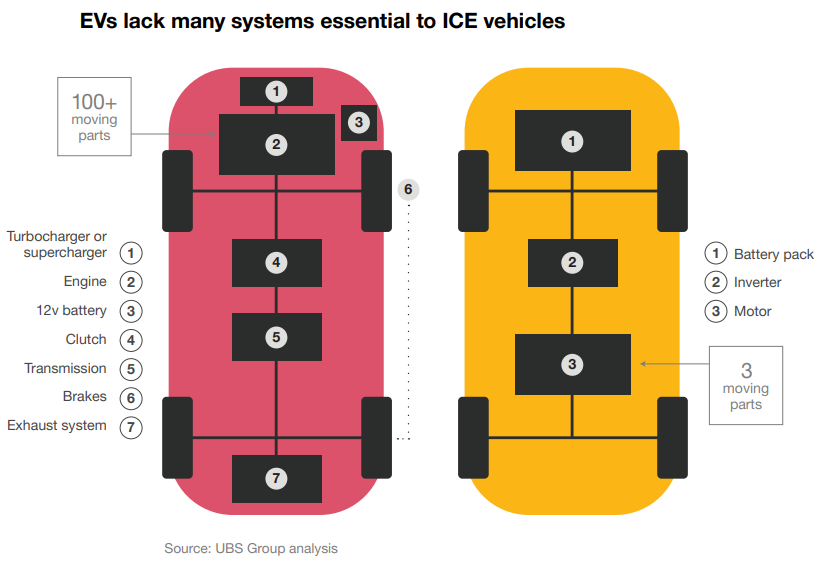
The image on the top reveals which supplier subsectors could be at risk.
Another challenge for suppliers is that the components in EVs are much lesser when compared to ICEs. For example, the UBS group compared the engines of the Chevrolet Bolt and a four-cylinder internal combustion engine. They found that the electric vehicle had 3 moving parts, compared to the ICE’s 113. And most of these EVs do not need turbochargers or to provide additional power. Thus, a large number of suppliers are at risk if they do not adapt to the changing times.
Also, a lithium-ion battery alone could eat up a major chunk of the cost of an EV. Though battery prices are steadily falling down, they are manufactured with components outside the traditional auto component ecosystem creating new competition for the legacy suppliers. And, one of the reasons that the share of EVs’ value added by component suppliers has reduced to 35-40% from 50-55% is that some EV battery suppliers are also developing expertise to manufacture electric powertrains. As a result, legacy suppliers are burdened with additional challenges. These pose additional challenges for legacy suppliers.
Increasing Consumer Expectations (Faster Time-to-Market)
One more challenge for EV manufacturers is the increase in consumer expectations. For example, the image below shows the consumer expectation(time-to-market) and the possible ROI time (time-in-market) for manufacturers.
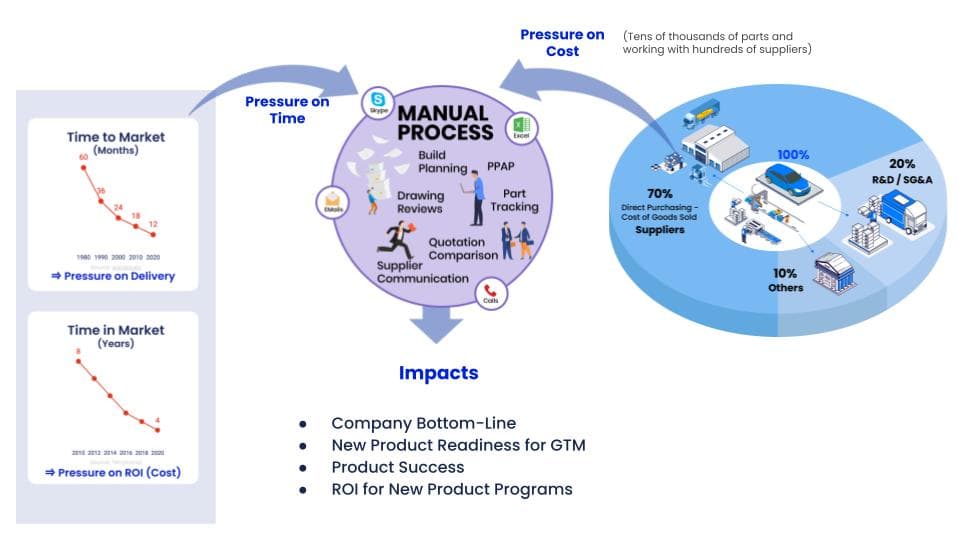
The estimated time to launch a new vehicle from idea generation is now 12 months from the earlier 60. Moreover, the average lifespan of the product in the market – the time available for the product in the market before retiring or being replaced – now stands at 4 years from the earlier 8 years. As a result, companies are speeding up the new product development processes, and investments are being poured in. Since the time to recover the investments is shortened, controlling costs will be a critical factor.
Rising Material Shortages and EV prices
The recent supply chain disruptions, shortages, and its aftermath, the inability to meet consumer demand are becoming major issues in EV manufacturing. The International Energy Agency (IEA) is expecting the number of EVs on road to be 145 million by 2030. And to support this growth, manufacturers will need to ramp up their production. This means the need for Lithium-ion batteries (LiBs), motors, and other electrical components will increase. On the other hand, experts are also predicting challenges such as a shortage of materials like Cobalt and Nickel, and challenges in Lithium production.
CEO of Stellantis, Carlos Tavares, expects a shortage in the supply of EV batteries by 2024-2025, along with a shortage of other raw materials for EV manufacturing. Thus, slowing the EV adoption rate by 2027-2028.
And a shortage of materials means that there will be a surge in prices too.
The Way Forward for EV Manufacturers
 The above-mentioned challenges are not the end. There’s more. It means the task is cut out for EV manufacturers. Sourcing raw materials, investing in establishing new plants or transforming the existing ones, purchasing new technologies, developing new suppliers(and onboarding them)or working with existing ones, and coming up with new designs for EVs to stay in the competition are a few of the tasks that lie ahead.
The above-mentioned challenges are not the end. There’s more. It means the task is cut out for EV manufacturers. Sourcing raw materials, investing in establishing new plants or transforming the existing ones, purchasing new technologies, developing new suppliers(and onboarding them)or working with existing ones, and coming up with new designs for EVs to stay in the competition are a few of the tasks that lie ahead.
And apart from R&D, Engineering and Design teams, Procurement teams will play a crucial role in ensuring that the project development is on track, discovering new suppliers, maintaining a strategic relationship with suppliers, conducting supplier evaluation, managing supplier performance, ensuring timely deliveries of materials at the right quality, managing product costs and raw material rate contracts, handling all the purchase contracts, etc. But can they execute these successfully in the way it is handled today? Using spreadsheets, emails, and reams of papers? Definitely not!
Introducing Zumen Source-to-Pay
With Zumen, EV manufacturing companies can work with software that’s built for direct sourcing and procurement. Companies will have real-time sourcing status updates, effective supplier relationship management capabilities to establish strategic sourcing, and a whole host of other features enabling companies to launch products in the market, 25% faster than before. To know more, feel free to reach out to us at [email protected] or schedule a free demo.